Effluent Treatment Plant (ETP) Chemicals: Complete Guide
Discover insights on water treatment solutions and technologies.

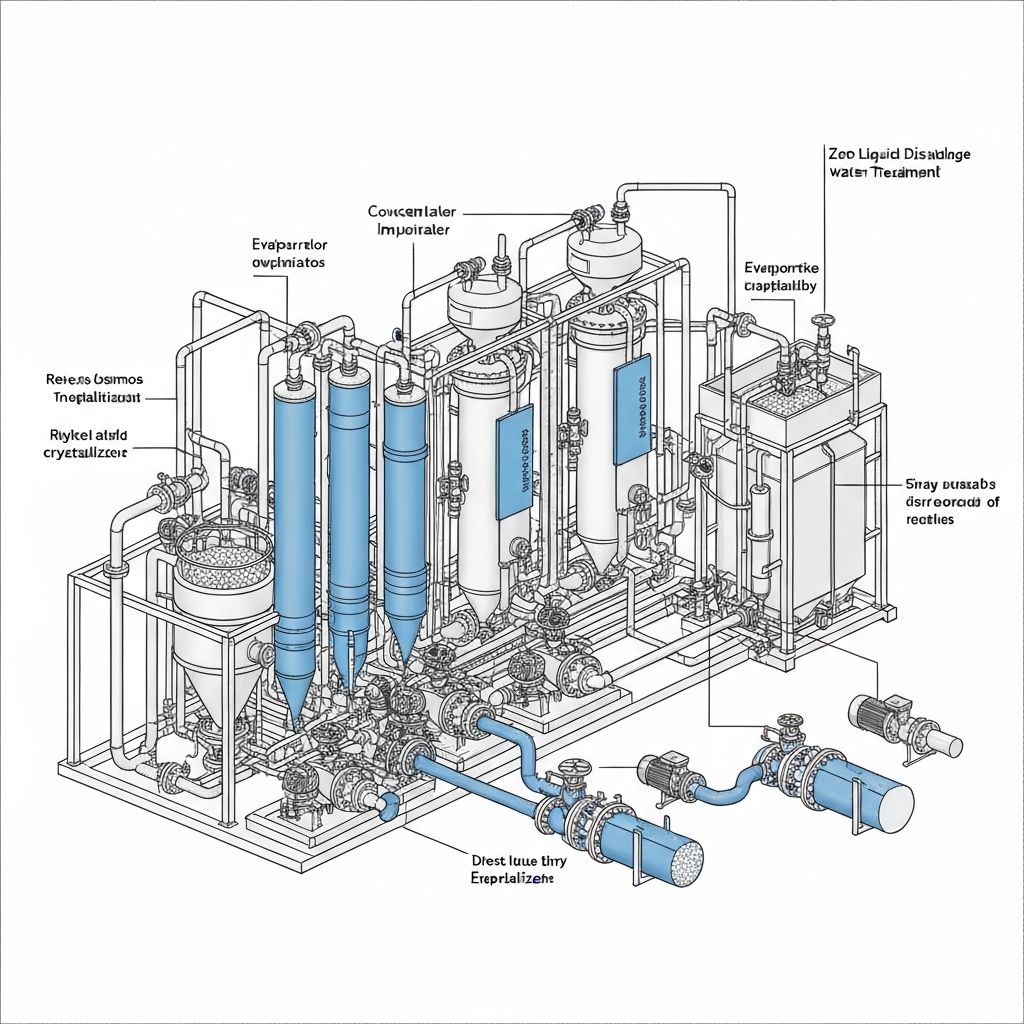
Effluent Treatment Plants (ETPs) are essential for industrial wastewater management, utilizing a combination of physical, biological, and chemical processes to treat wastewater before discharge. This comprehensive guide covers the essential chemicals used in ETPs and their applications in achieving environmental compliance.
Understanding ETP Treatment Stages
Primary Treatment (Physical)
Initial removal of large solids and floating materials:
- Screening and grit removal
- Sedimentation in primary clarifiers
- Oil and grease separation
- pH adjustment and neutralization
Secondary Treatment (Biological)
Biological degradation of organic matter:
- Aerobic treatment (activated sludge)
- Anaerobic digestion
- Biological nutrient removal
- Biofilm reactors
Tertiary Treatment (Chemical/Advanced)
Polishing and advanced treatment processes:
- Chemical precipitation
- Advanced oxidation
- Membrane filtration
- Disinfection
pH Adjustment Chemicals
Acids for pH Reduction
Sulfuric Acid (H₂SO₄)
- Strong acid for rapid pH adjustment
- Cost-effective for large-scale applications
- Requires careful handling and storage
- Commonly used in industrial ETPs
Hydrochloric Acid (HCl)
- Strong acid with minimal scaling potential
- Effective for neutralizing alkaline wastes
- Produces soluble chlorides
- Used in food processing ETPs
Alkalis for pH Increase
Sodium Hydroxide (NaOH)
- Strong base for rapid neutralization
- Highly soluble and easy to handle
- Produces sodium salts in treated water
- Most commonly used alkaline chemical
Lime (Calcium Hydroxide)
- Cost-effective alkaline agent
- Also aids in precipitation of metals
- Produces insoluble calcium salts
- Requires sludge handling considerations
Coagulation and Flocculation Chemicals
Primary Coagulants
Aluminum Sulfate (Alum)
- Most widely used coagulant
- Effective pH range: 5.5-7.5
- Forms aluminum hydroxide flocs
- Good for turbidity removal
Ferric Chloride (FeCl₃)
- Effective over wider pH range
- Good for color removal
- Forms dense, settleable flocs
- Also provides some disinfection
Ferrous Sulfate (FeSO₄)
- Economical coagulant option
- Effective in alkaline conditions
- Requires oxidation to ferric form
- Commonly used in textile ETPs
Polyaluminum Chloride (PAC)
- Pre-polymerized coagulant
- Effective at lower doses
- Produces less sludge
- Wide pH operating range
Flocculants
Polyacrylamide Polymers
- Anionic, cationic, and non-ionic types
- High molecular weight polymers
- Bridge particles for larger flocs
- Dosage: 0.1-5 mg/L typical
Natural Flocculants
- Chitosan from shellfish waste
- Moringa oleifera seeds
- Starch-based flocculants
- Environmentally friendly options
Precipitation Chemicals
Heavy Metal Removal
Sodium Hydroxide
- Precipitates metals as hydroxides
- Common for chromium, nickel, zinc
- pH-dependent precipitation
- Produces metal hydroxide sludge
Sodium Sulfide
- Precipitates heavy metals as sulfides
- More effective than hydroxides
- Toxic and requires careful handling
- Generates H₂S gas in acidic conditions
Dimethyl Dithiocarbamate (DMDTC)
- Organic precipitant for heavy metals
- Effective at low concentrations
- Selective precipitation possible
- Expensive but highly effective
Phosphorus Removal Chemicals
Chemical Precipitation
Aluminum and Iron Salts
- Alum, ferric chloride, ferrous sulfate
- Form aluminum/iron phosphate precipitates
- Simultaneous coagulation and phosphorus removal
- Dose: 10-50 mg/L as Al/Fe
Lime
- Precipitates phosphorus as calcium phosphate
- High pH requirements (pH >9)
- Cost-effective for large applications
- Produces large amounts of sludge
Disinfection Chemicals
Chlorine-Based Disinfectants
Sodium Hypochlorite
- Liquid bleach (10-15% available chlorine)
- Easy to dose and handle
- Provides residual protection
- Forms disinfection byproducts
Calcium Hypochlorite
- Solid form (65-70% available chlorine)
- Longer shelf life than sodium hypochlorite
- Increases water hardness
- Requires dissolution before dosing
Advanced Oxidation
Hydrogen Peroxide
- Strong oxidizing agent
- No residual effect
- Breaks down to water and oxygen
- Often used with UV activation
Ozone
- Generated on-site from oxygen
- Most powerful oxidant
- No chemical residues
- High capital and operating costs
Sludge Conditioning Chemicals
Sludge Dewatering Aids
Cationic Polymers
- Improve sludge dewatering
- Reduce sludge volume
- Enhance cake solids content
- Optimize filter press operation
Lime
- Conditions sludge for dewatering
- Stabilizes organic sludge
- Reduces odor problems
- Improves sludge handling
Neutralization Chemicals
Acid Neutralization
- Sodium carbonate (soda ash)
- Calcium carbonate (limestone)
- Sodium bicarbonate
- Magnesium hydroxide
Base Neutralization
- Sulfuric acid
- Hydrochloric acid
- Carbon dioxide (for mild alkalinity)
Dosing and Control Systems
Dosing Equipment
- Metering pumps for liquid chemicals
- Dry feeders for powders and granules
- Automatic dosing systems
- Batch dosing equipment
Control Strategies
- Feedback control based on effluent quality
- Feed-forward control based on influent
- Ratio control for proportional dosing
- Adaptive control for optimization
Safety and Environmental Considerations
Chemical Handling
- Material Safety Data Sheets (MSDS)
- Personal protective equipment
- Spill containment measures
- Emergency response procedures
Environmental Impact
- Biodegradable chemical options
- Minimization of chemical usage
- Proper sludge disposal
- Regulatory compliance
Industry-Specific Applications
Textile Industry
- Color removal chemicals
- High BOD/COD reduction
- Dye fixation chemicals
Pharmaceutical Industry
- API removal chemicals
- Solvent recovery
- Advanced oxidation requirements
Food Processing
- Organic load reduction
- Oil and grease removal
- Nutrient removal
Emerging Technologies
- Electrocoagulation
- Advanced oxidation processes
- Membrane bioreactors
- Zero liquid discharge systems
Conclusion
Effective ETP chemical treatment requires careful selection of chemicals based on wastewater characteristics, treatment objectives, and regulatory requirements. A well-designed chemical treatment program ensures compliance while optimizing operational costs.
ChemParks offers comprehensive ETP chemical solutions customized to your industry and wastewater characteristics. Contact us for detailed analysis and treatment program design.